
Traditional steam systems
Traditional steam systems designed for generating and distributing steam at high pressures.
Boiler-based steam systems usually generate steam by combustion of fossil fuels.
These systems are designed for generating and distributing steam at high pressures;
which would reduce the size and cost of some of the components and allow a smooth
operation of the system.
|

|
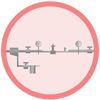
1. The boiler produces steam at high pressure.
The water level is controlled to avoid overheating
of the tubes. It is possible to lower the pressure
of the steam by working at part load, which is
controlled by the burner.
|
|
|
2. Steam is distributed at high pressures.
Pressure reduction stations reduce the correct
pressure level at the point of use. These valves
allow a smoother boiler operation and protect it
from sudden changes on the load. The capacity of
these valves is reduced when lowering steam pressure.
|
|
|
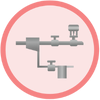
3. Temperature control is key to the operation of the
system. The control valve controls the temperature at
the outlet of the heat exchanger by controlling the mass
flow of the steam. Valve capacity must be checked when
lowering steam temperature.
|
|
|
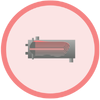
4. Heat is transferred from the steam to the process in the
heat exchanger. The heat exchanger can be sized by
the pressure drop at the process side or by the heat
exchange area. Lowering steam pressure would lower
the capacity of the heat exchanger.
|
|
|
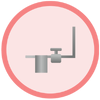
5. Steam fully condenses in the heat exchanger, and if
subcooling takes place, it is known as “stall conditions”.
The steam trap drains the condensate from the heat
exchanger. In order to do so, the backpressure of the
condensate must be lower than the steam pressure.
|
|

|
6. The condensate recovery system collects the hot
condensate from the steam and returns it to the boiler
feed system. As condensate is discharged from a higher
to a lower pressure, some of it will flash. This steam
should be recovered.
|
Download poster
From boiler-based to Heat-Pump-based Industrial Steam Systems
Read more
Read about the new heat pump-based steam systems and the electrification of industrial steam systems.







